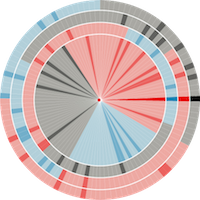
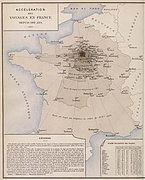
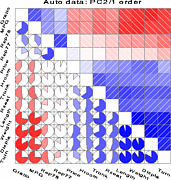
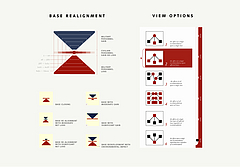
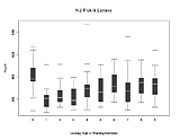
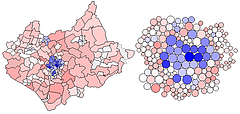
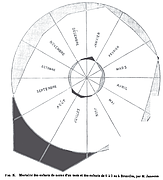
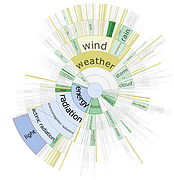
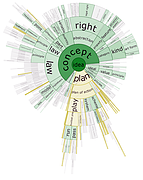
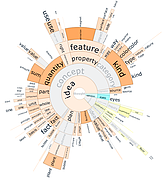
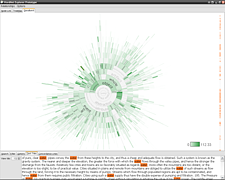
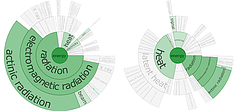
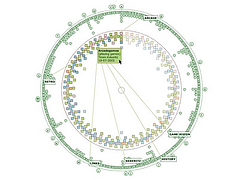
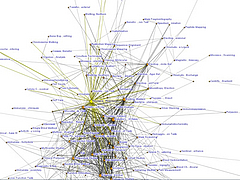
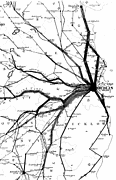
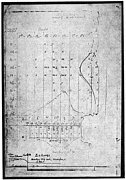
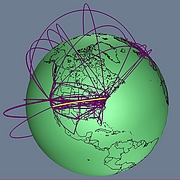
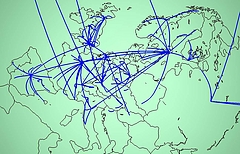
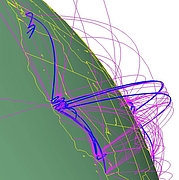
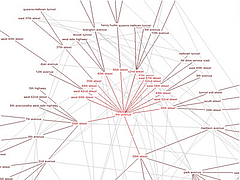
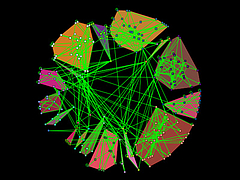
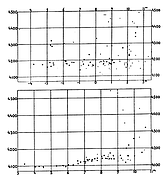
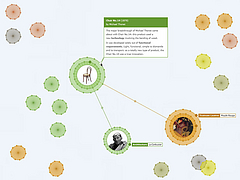
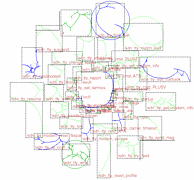
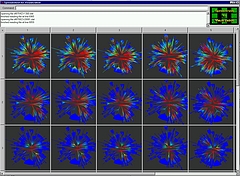
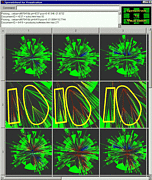
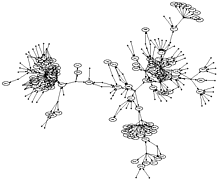
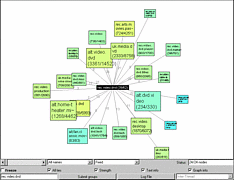
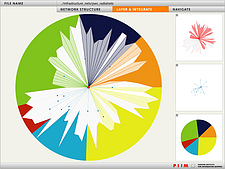
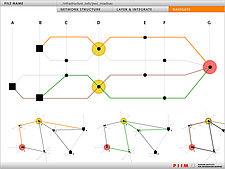
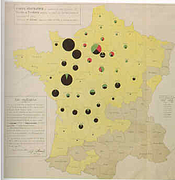
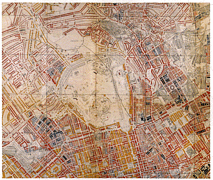
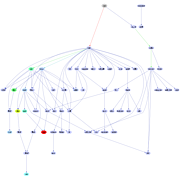
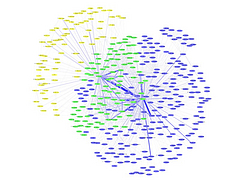
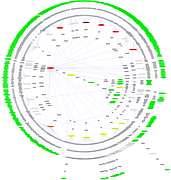
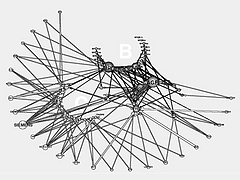
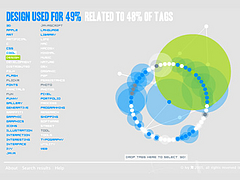
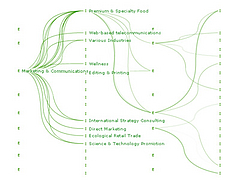
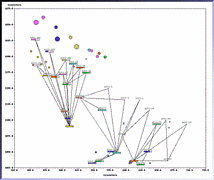
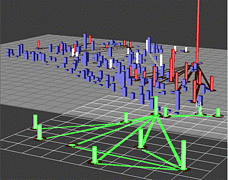
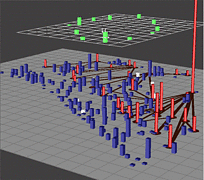
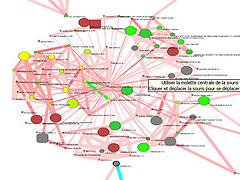
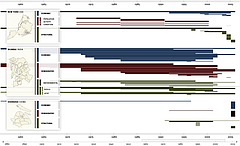
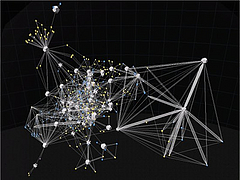
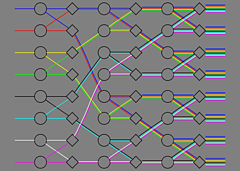
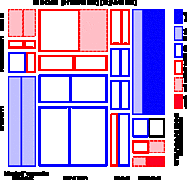
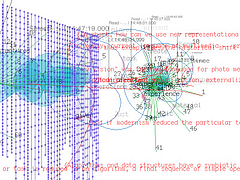
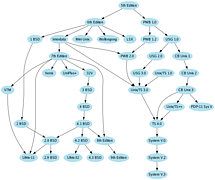
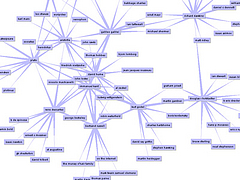
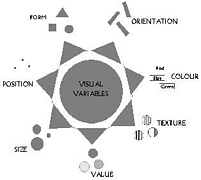
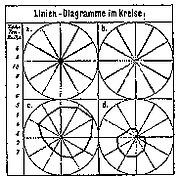
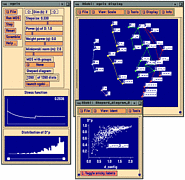
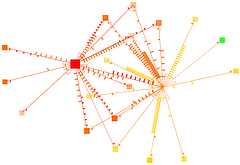
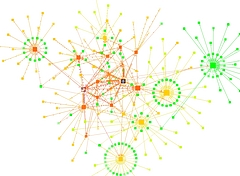
 907 907 | 2004 computer graphics by Gerhard Dirmoser In the last years, Gerhard Dirmoser has developed a set of strikingly complex visualization posters under the theme "Art-in-Context" (Die Kunst der Ausstellung). The form of this context is usually a diagram in the size of a poster (aprox. 240cm x 180cm), split in 4 parts. In this poster, Dirmoser analyzes most author's contributions to Ars Electronica in the last 25 years. Due to the limitations of the available surface, it wasn't possible to provide a complete detailed presentation of all the participating artists, scientists and developers (about 3100 persons are listed). All the participants were compared with the AEC/Ars database. The language material used was taken from publications on "ars electronica", notes (on the symposium lectures) and relevant literature. The study "Designing Gestures" on ars electronica 2003 was carried out in parallel. The choice/placement is thus to be regarded as the author of the study's subjective/content-based selection.The study is intended to provide a wide-ranging survey, but it cannot substitute for reading the catalogues. In some cases, key works (or concepts) are cited, which were not shown in Linz, but are described in detail in catalogues. The poster can also be used as an index with the page numbers. The first image shows one of the four pieces of the poster and the second image is a detailed view of it. To see the poster in a public installation, click here |
 194 194 | 1998 computer graphics (KnotPlot) by Robert G. Scharein From the knotplot.com/zoo website, you can click on a knot to load it into an interactive 3D viewer (requires Java). |
 195 195 | 1998 computer graphics (KnotPlot) by Robert G. Scharein From the knotplot.com/zoo website, you can click on a knot to load it into an interactive 3D viewer (requires Java). |
 959 959 | 2002 computer graphics by Marius Watz Marius Watz, Art Director of Generator.x, has used the nom-de-guerre Amoeba since 1995 for experimentation in electronic media, with the web site Evolutionzone.com as the output. In this environment, Watz shows amazing generative art pieces that are both intriguing and captivating. AmoebaAbstracts 1-3, is a set of 3 experiments in abstract computational composition and dynamic form. The abstracts, responsive to user input, were built with Processing for the exhibition "Abstraction Now", Kunstlerhaus Wien, September 2003, and were also exhibited at Sonar 2004, Barcelona. The images shown are representative of Abstract 2, an endlessly emerging geometric pattern. This generative piece of visual abstraction doesn't consider any set of actual data, however, its aesthetical visual depiction represents a fresh approach that might prove inspiring to any network visualization endeavor. |
 909 909 | 2005 computer graphics by Ero Carrera, Gergely Erdelyi Windows binary malware has come a long way. Today's average worm is often tens or hundreds of kilobytes of code exhibiting a level of complexity that surpasses even some operating systems. This degree of complexity, coupled with the overwhelming flow of new malware, calls for improvements to tools and techniques used in analysis. F-Secure produced this rich 3D animation that visualizes the structure and execution of the W32/Bagle.AG@mm worm. The boxes in the picture are functions of the worm. The one on the top is the 'main' where the execution starts. The first ring contains all the functions that 'main' calls. The second all the functions that the ones on the first ones call and so on. All connecting lines represent the calls from one function to the other. Red boxes belong to the virus code while the blue ones are API calls library code that do not belong to the malicious code. The animation was created using IDA Pro, IDAPython, Blender and other custom scripts. For a direct link to the animation (quicktime required), click here. |
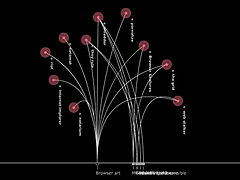
 1255 1255 | 2007 Web by Daniele Galiffa using Actionscript Analysis and experiments on relations into the Italian Blogosphere I’ve been invited to join to the blogbabel initiative that aims to map the italian blogosphere. My effort in this interesting project is about to find some new, useful infovis-related solutions to offer some better cognitive tools to approach the Italian blog world and its relations. I started looking around to find interesting solutions about blog-mapping ( from the Manuel Lima’s blogviz, to the BlogoPole French initiative and the first BlogBabel visualization from Ludo). What seemed to me really interesting is mainly the relations Analysis and not the Graph representation, because it tends to offer a “star-system†style visual environment that requires some more deep work in order to be used to understand how blogs are related each other. My idea is really simple: suppose you have a line where you can use points to represent Blogs. Above the line I can have arches connecting a source blog (on the left side of the arch) to another (on the right side of the arch). Below the line I can have also arches, but the connection direction is from right to left. The use of arches and circles come out from “The Shape of Songs†by Martin Wattenberg. In this way we have a LinksOut View (UP) and a LinksIn View (DOWN) and we could use the opacity of each arch to visualize how relations are relevant considering the numeber of links (in/out) among blogs. The above description was modified from: http://www.mentegrafica.it/blog/2007/05/10/analisys-and-experiments-on-relation-into-the-italian-blogosphere/ (images may be found at http://flickr.com/photos/danielegaliffa/tags/blogosphere/) |
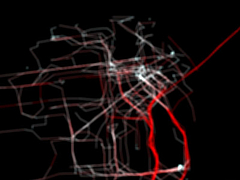 1021 1021 | 2006 computer graphics by Shawn Allen, Thomas Apodaca, Mik Invisible Dynamics is a research project sponsored by The Exploratorium which explores the meanings and representations of place. Working across the domains of art, design, cultural geography, cartography, information design, sociology, hydrology, marine sciences, and history, I.D. hosts residencies and workshops, as well as developing exhibitions and public programs. Using new technologies for the representation and analysis of spatial information, I.D. investigates the complexities of the San Francisco Bay Region in the context of the Pacific Rim. As part of Invisible Dynamics, Stamen Design has been exploring visualizations of GPS data generated by Yellow Cab taxi cabs in San Francisco. In these frame-by-frame maps of the locations of cabs in the Bay Area, the city ebbs and pulses like the beating of a heart in a truly captivating sequence. Both visualizations are part of a video where each frame shows 15 minutes of activity in a dynamic map of taxicabs' speed and position. In the first image, speed is represented by the change in color (White: 0 mph Red: >35 mph), while in the second, larger crosses represent faster taxis. Cabspotting is a product of San Francisco's Stamen Design, a boutique services firm specializing in data visualization, map making, interactive media, and creative technology reinterpretation. You might remember Stamen from such projects as Mappr or In The News / Vox Delicii. |
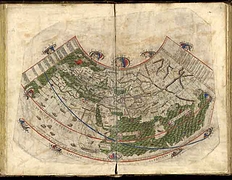
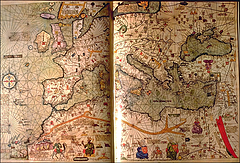 1 1 | 1375 print by Abraham Cresques (1325-1387), Majorca, Spain Catalan Atlas, an exquisitely beautiful visual cosmography, perpetual calendar, and thematic representation of the known world. |
 557 557 | computer graphics |
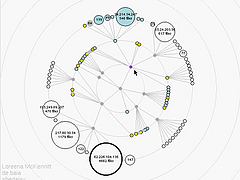
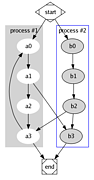
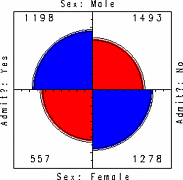
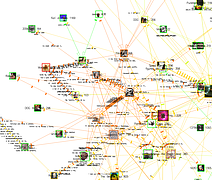 1248 1248 | Comment Flow2007 software (Java) by Dietmar Offenhuber A browser visualizing conversations via guest book entries across myspace profiles We have designed and implemented a flexible tool for the content driven exploration and visualisation of a social network. Building upon a traditional force-directed network layout consisting of nodes (profiles) and edges (friend-links), our system shows the activity and the information exchange (postings in the comment box) between nodes, taking the sequence and age of the messages into account. This project serves both as an illustration of one approach to the general problem of individuated network visualization and as an example of the practical uses of such representations. In the mySpace service network-only visualization methods are no longer sufficient to meaningfully represent the community structure. Numerous commercial profiles, fake/spam/celebrity profiles and tools such as automated friend adders result in a huge numbers of connections, many of which carry little information about a person’s actual social ties and behavior. The average myspace user has more than 130 friends, but there are also profiles with over a million “friends”. By going beyond the “skeleton” of network connectivity and looking at the flow of information between the individual actors we can create a far more accurate portrait of online social life. |
 1246 1246 | Comment Flow2007 software (Java) by Dietmar Offenhuber A browser visualizing conversations via guest book entries across myspace profiles We have designed and implemented a flexible tool for the content driven exploration and visualisation of a social network. Building upon a traditional force-directed network layout consisting of nodes (profiles) and edges (friend-links), our system shows the activity and the information exchange (postings in the comment box) between nodes, taking the sequence and age of the messages into account. This project serves both as an illustration of one approach to the general problem of individuated network visualization and as an example of the practical uses of such representations. In the mySpace service network-only visualization methods are no longer sufficient to meaningfully represent the community structure. Numerous commercial profiles, fake/spam/celebrity profiles and tools such as automated friend adders result in a huge numbers of connections, many of which carry little information about a person’s actual social ties and behavior. The average myspace user has more than 130 friends, but there are also profiles with over a million “friends”. By going beyond the “skeleton” of network connectivity and looking at the flow of information between the individual actors we can create a far more accurate portrait of online social life. |
 1247 1247 | Comment Flow2007 software (Java) by Dietmar Offenhuber A browser visualizing conversations via guest book entries across myspace profiles We have designed and implemented a flexible tool for the content driven exploration and visualisation of a social network. Building upon a traditional force-directed network layout consisting of nodes (profiles) and edges (friend-links), our system shows the activity and the information exchange (postings in the comment box) between nodes, taking the sequence and age of the messages into account. This project serves both as an illustration of one approach to the general problem of individuated network visualization and as an example of the practical uses of such representations. In the mySpace service network-only visualization methods are no longer sufficient to meaningfully represent the community structure. Numerous commercial profiles, fake/spam/celebrity profiles and tools such as automated friend adders result in a huge numbers of connections, many of which carry little information about a person’s actual social ties and behavior. The average myspace user has more than 130 friends, but there are also profiles with over a million “friends”. By going beyond the “skeleton” of network connectivity and looking at the flow of information between the individual actors we can create a far more accurate portrait of online social life. |
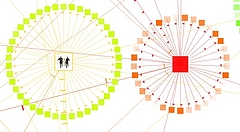 1249 1249 | Comment Flow2007 software (Java) by Dietmar Offenhuber A browser visualizing conversations via guest book entries across myspace profiles We have designed and implemented a flexible tool for the content driven exploration and visualisation of a social network. Building upon a traditional force-directed network layout consisting of nodes (profiles) and edges (friend-links), our system shows the activity and the information exchange (postings in the comment box) between nodes, taking the sequence and age of the messages into account. This project serves both as an illustration of one approach to the general problem of individuated network visualization and as an example of the practical uses of such representations. In the mySpace service network-only visualization methods are no longer sufficient to meaningfully represent the community structure. Numerous commercial profiles, fake/spam/celebrity profiles and tools such as automated friend adders result in a huge numbers of connections, many of which carry little information about a person’s actual social ties and behavior. The average myspace user has more than 130 friends, but there are also profiles with over a million “friends”. By going beyond the “skeleton” of network connectivity and looking at the flow of information between the individual actors we can create a far more accurate portrait of online social life. |
 1252 1252 | Comment Flow2007 software (Java) by Dietmar Offenhuber A browser visualizing conversations via guest book entries across myspace profiles We have designed and implemented a flexible tool for the content driven exploration and visualisation of a social network. Building upon a traditional force-directed network layout consisting of nodes (profiles) and edges (friend-links), our system shows the activity and the information exchange (postings in the comment box) between nodes, taking the sequence and age of the messages into account. This project serves both as an illustration of one approach to the general problem of individuated network visualization and as an example of the practical uses of such representations. In the mySpace service network-only visualization methods are no longer sufficient to meaningfully represent the community structure. Numerous commercial profiles, fake/spam/celebrity profiles and tools such as automated friend adders result in a huge numbers of connections, many of which carry little information about a person’s actual social ties and behavior. The average myspace user has more than 130 friends, but there are also profiles with over a million “friends”. By going beyond the “skeleton” of network connectivity and looking at the flow of information between the individual actors we can create a far more accurate portrait of online social life. |
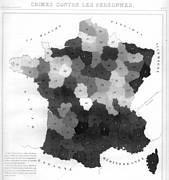
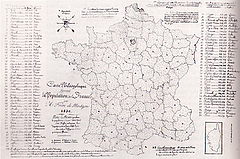
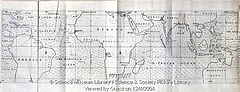
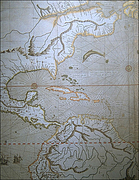
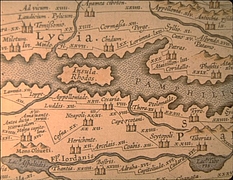
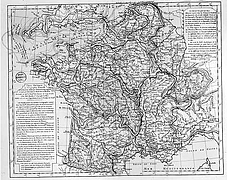 37 37 | 1752 print by Phillippe Buache (1700-1733), France Contour map. Buache, P. (1752). Essai de géographie physique. Mémoires de L'Académie Royale des Sciences , pp. 399-416. BNF: Ge.FF-8816-8822. |
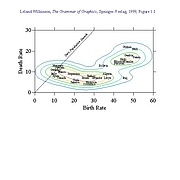
 411 411 | computer graphics by Luc Girardin An example map from Luc Girardin's, The Graduate Institute of International Studies, Switzerland, "cyberspace geography visualization" system. |
 1399 1399 | 2010 by Give Me My Data / Nodebox 1.0 Network graph visualization of Facebook contacts using data retrieved using Give Me My Data http://givememydata.com and Nodebox 1.0. |
 1400 1400 | 2010 by Give Me My Data / Nodebox 1.0 Network graph visualization of Facebook contacts using data retrieved using Give Me My Data http://givememydata.com and Nodebox 1.0. |
 1401 1401 | 2010 by Give Me My Data / Nodebox 1.0 Network graph visualization of Facebook contacts and mutual contacts using data retrieved using Give Me My Data http://givememydata.com and Nodebox 1.0. |
 1402 1402 | 2010 by Give Me My Data / Nodebox 1.0 Network graph visualization of Facebook contacts and mutual contacts using data retrieved using Give Me My Data http://givememydata.com and Nodebox 1.0. |
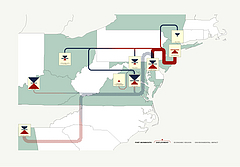
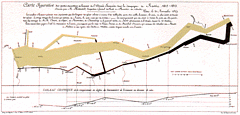
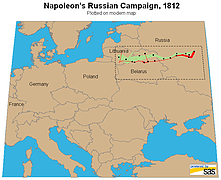
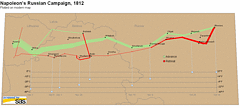
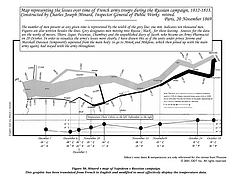
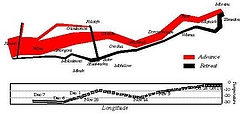
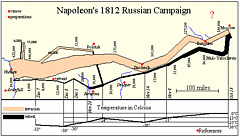
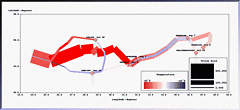
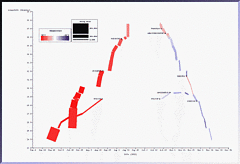
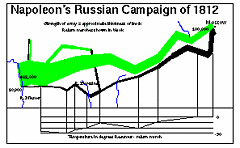
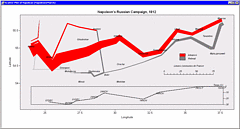
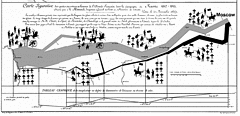
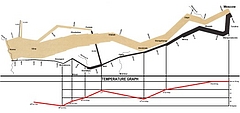
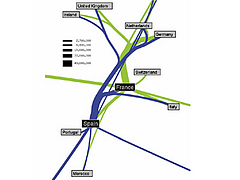 927 927 | 2005 computer graphics by Doantam Phan, Ling Xiao, Ron Yeh Flow Map Layout is a novel visualization technique seen as a hybrid of graphs and flow maps. Cartographers have long used flow maps to show the movement of objects from one location to another, such as the number of people in a migration, the amount of goods being traded, or the number of packets in a network. One of the most famous flow maps, depicting Napoleon's Russian Campaign, was created by Charles Joseph Minard in 1869, and can be seen here. The advantage of flow maps is that they reduce visual clutter by merging edges. Most flow maps are drawn by hand and there are few computer algorithms available. In Flow Map Layout, the authors present a method for generating flow maps using hierarchical clustering given a set of nodes, positions, and flow data between the nodes. The technique is inspired by graph layout algorithms that minimize edge crossings and distort node positions, while maintaining their relative position to one another. The authors have demonstrated the technique by producing flow maps for network traffic, census data, and trade data. The first image illustrates a close-up of top 15 imports to Spain and France. Notice the branching structure is shared across different nodes, for example Spain, and France branch to the Netherlands, Germany and the UK in the same way. The second image represents an outgoing migration map from Colorado (USA) from 1995-2000, generated by the algorithm without layout adjustment or edge routing. |
 75 75 | 1878 print by Eadweard Muybridge (1830-1904), USA Recording of motion (of a running horse) by means of a set of glass-plate cameras, triggered by strings. |
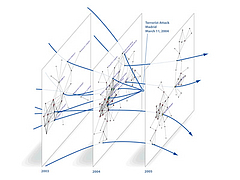
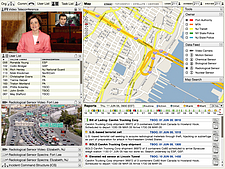
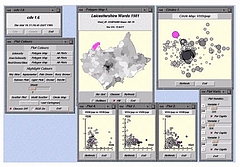
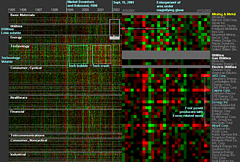
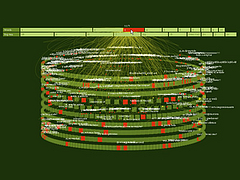
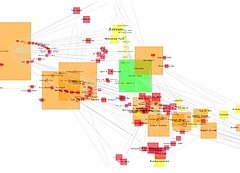
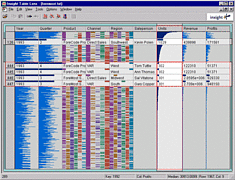
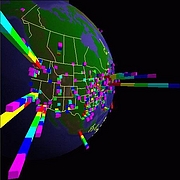
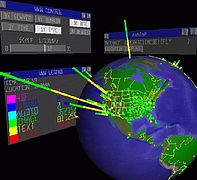
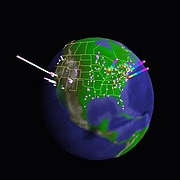
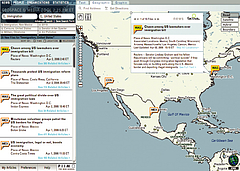 1215 1215 | Geospace & Media Tool (GMT): Geolocated news2007 computer graphics by Parsons Institute for Information Mapping (PIIM) This screenshot shows a selected news abstract set in geographical context. GMT Description The Geospace & Media Tool is an advanced information visualization application that ties incoming news flow with geospatial, census, and human network data. Related news articles are scored and aggregated into single, convenient event files. Easy-to-use graphic and geographic visualizations give the user the ability to see events, demographics, rnorganizations and current as well as past professional connections between people. Key features include: Detailed content and metadata on every news article Full dossier of individuals mentioned in every news articlern Ability to track and search events by location, topic, and customized filters Automatic extraction and aggregation of related network and statistical data Visual display of network connections between professionals Access to hundreds of statistical values specifically relevant to each news article, accompanied by map overlays |
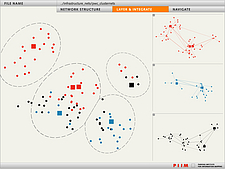
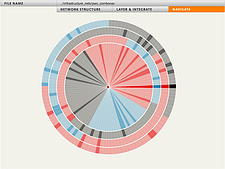
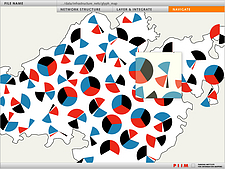
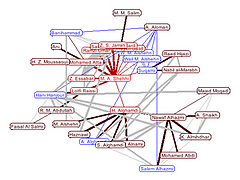
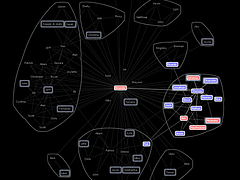
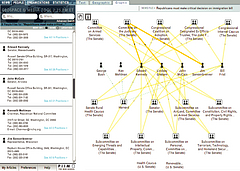 1213 1213 | Geospace & Media Tool (GMT): Human organizational networks2007 computer graphics by Parsons Institute for Information Mapping (PIIM) This screenshot shows the relationships among individuals as a human organizational network diagram. GMT Description The Geospace & Media Tool is an advanced information visualization application that ties incoming news flow with geospatial, census, and human network data. Related news articles are scored and aggregated into single, convenient event files. Easy-to-use graphic and geographic visualizations give the user the ability to see events, demographics, rnorganizations and current as well as past professional connections between people. Key features include: Detailed content and metadata on every news article Full dossier of individuals mentioned in every news articlern Ability to track and search events by location, topic, and customized filters Automatic extraction and aggregation of related network and statistical data Visual display of network connections between professionals Access to hundreds of statistical values specifically relevant to each news article, accompanied by map overlays |
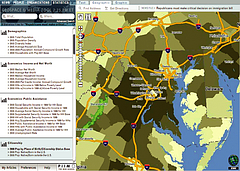 1214 1214 | Geospace & Media Tool (GMT): Statistics2007 computer graphics by Parsons Institute for Information Mapping (PIIM) This screenshot shows census data for a selected congressional district. GMT Description The Geospace & Media Tool is an advanced information visualization application that ties incoming news flow with geospatial, census, and human network data. Related news articles are scored and aggregated into single, convenient event files. Easy-to-use graphic and geographic visualizations give the user the ability to see events, demographics, rnorganizations and current as well as past professional connections between people. Key features include: Detailed content and metadata on every news article Full dossier of individuals mentioned in every news articlern Ability to track and search events by location, topic, and customized filters Automatic extraction and aggregation of related network and statistical data Visual display of network connections between professionals Access to hundreds of statistical values specifically relevant to each news article, accompanied by map overlays |
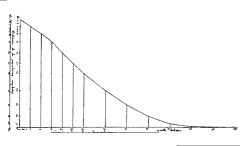
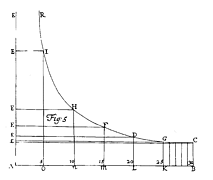
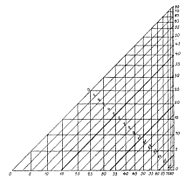
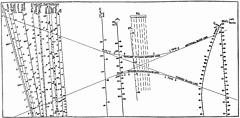
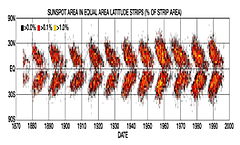
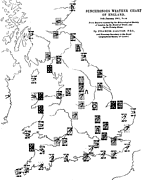
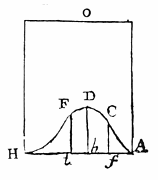 32 32 | 1763 print by Thomas Bayes (1702-1761), England Graph of the beta density. |
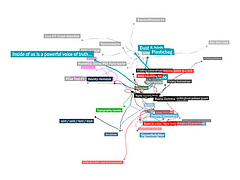
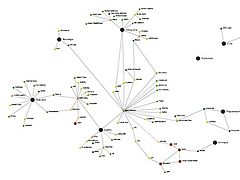
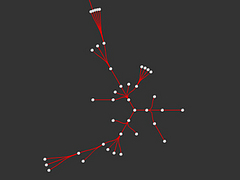
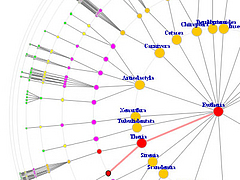
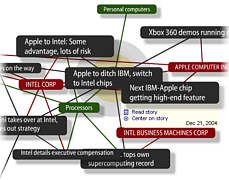
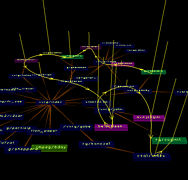
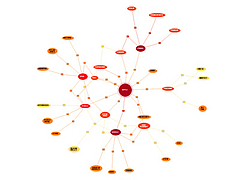 1069 1069 | 2006 computer graphics by Roberto Bianchettin The GraphNews project (beta released) has been developed as a new visualization and browsing feature of the Libero WebNews service, part of the Libero portal, one of the major Italian Internet Service providers. Libero WebNews, developed from Arianna Team, allows a fast visualization of the news published on the Web from more than 1.100 journalistic sources online. GraphNews analyzes the content of the news articles processed in Libero WebNews, with the goal of highlighting the main subjects, i.e. the people, the products, the localities, the societies, the institutions, etc., and extracts the relations that elapse between them. The final result of this elaboration is a graph visualization of these subjects and their relations. The graph is browsable through a simple one click: GraphNews also allows the change of detail level and the time period (day, week, month) of the graph. In the cases shown here, the inputted word for the first image was "Apple", while on the second was "Google". |
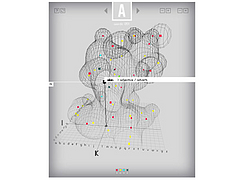
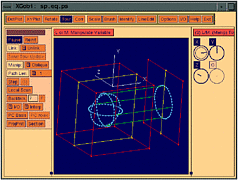
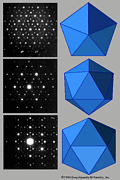
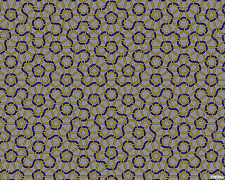 191 191 | 1995 computer graphics by Robert G. Scharein The link pictured here is an infinitely complex link consisting of an infinite number of unknots. Each unknot has five-fold symmetry about its centre. |
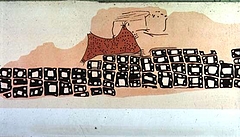 6 6 | print The oldest known map? (There are several claimants for this honor.)- unknown, Museum at Konya, Turkey. |
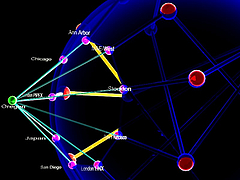
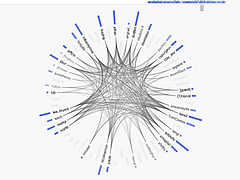
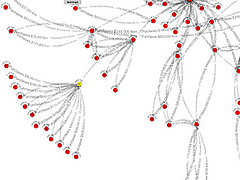
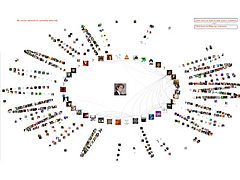
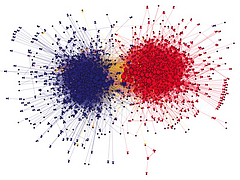
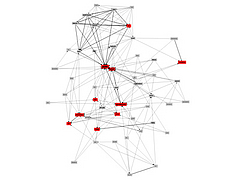
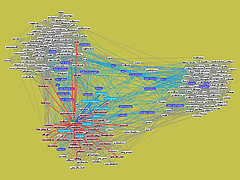
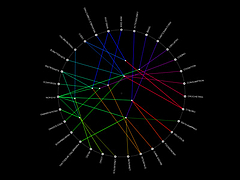
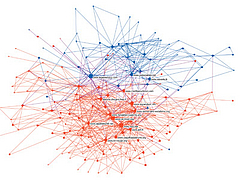
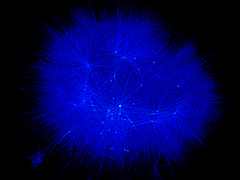 809 809 | 2004 computer graphics by Jeffrey Heer This image is a visualization of Jeffrey Heer's personal friendster network to 3 hops out, an online social network consisting of Jeffrey, his "friends", his friends' friends, and his friends' friends' friends. The resulting networks consist of 47471 people connected by 432430 friendship relations. The data was collected during the timespan of October 2003 to February 2004 as part of the Vizster project. The images were created using the prefuse visualization toolkit. Nodes are colored by proximity to the center of the network (which in this case is Jeffrey Heer himself). The central person is the brightest, that person's friends next brightest and so on. The elements are also ordered so that friends and relations closer from the central person are drawn on top of more distant relations and people. The graph layout was computed using a standard force-directed layout method in which nodes exert anti-gravity against each other and the edges are treated as springs. |
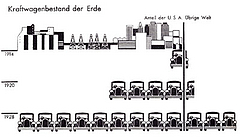
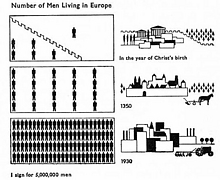
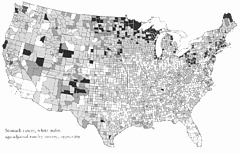
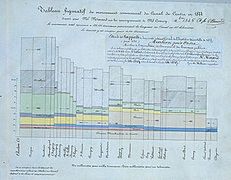
 95 95 | 1884 print by Michael George Mulhall (1836-1900), England Pictogram, used to represent data by icons proportional to a number. Mulhall, M. G. (1884). Dictionary of statistics. London. |
 3 3 | 1235 print by Ramon Llull (1235-1316), Spain Mechanical diagrams of knowledge, as aids to reasoning (served as an inspiration to Leibnitz in the development of symbolic logic) (Spain). |
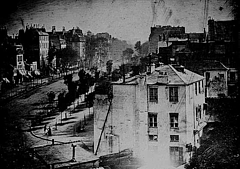 56 56 | 1839 Print by Louis Jacques Mandé Daguerre (1787-1851), France Invention of the first practical photographic process, using coated plates of metal and glass. |
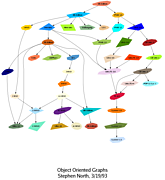
 653 653 | computer graphics by Graphviz - Graph Visualization Software This example illustrates the use of partially transparent colors for node fill and graph background. |
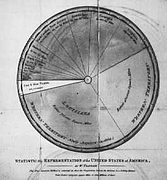
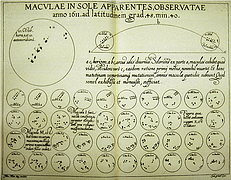
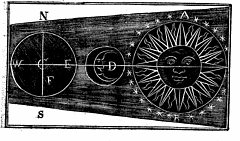
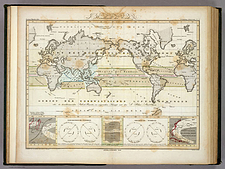
 4 4 | 950 print Earliest known attempt to show changing values graphically (positions of the sun, moon, and planets throughout the year)(Europe) |
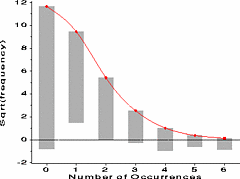
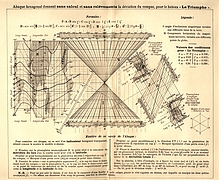
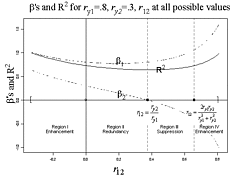
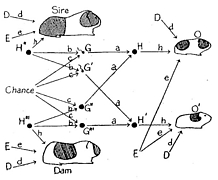
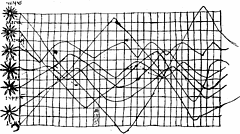
 127 127 | 1972 print by David F. Andrews, Canada Form of Fourier series to generate plots of multivariate data. Andrews, D.F. (1972). Plots of high dimensional data. Biometrics, 28:125-136. |
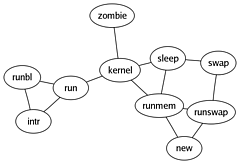 651 651 | computer graphics, after hand-made figure by Graphviz - Graph Visualization Software This graph was created from a hand-made figure in an operating system paper. |
 94 94 | 1884 print by Michael George Mulhall (1836-1900), England Pictogram, used to represent data by icons proportional to a number. Mulhall, M. G. (1884). Dictionary of statistics. London. |
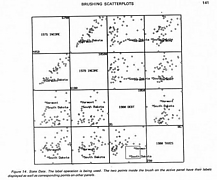
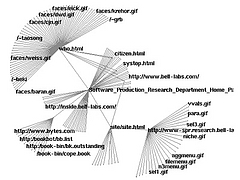
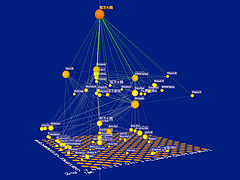
 310 310 | computer graphics by Stephen E. Lamm and Daniel A. Reed, Department of Computer Science, University of Illinois, USA |
 311 311 | computer graphics by Stephen E. Lamm and Daniel A. Reed, Department of Computer Science, University of Illinois, USA |
 312 312 | computer graphics by Stephen E. Lamm and Daniel A. Reed, Department of Computer Science, University of Illinois, USA |
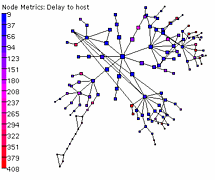
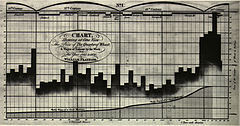
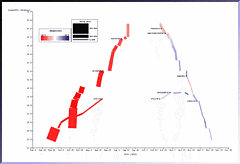
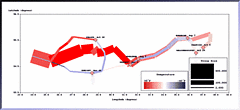
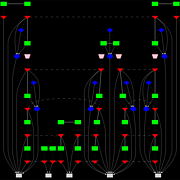
 980 980 | 2003 computer graphics by Ed Blanchfield Ed Blanchfield used a Firewall/Intrusion Detection System (IDS) log data to get "before" and "after" graphs showing the impact of an MS-SQL worm, which hit the Internet around January 25th 2003. When this particular worm hit a large class B sized network, an IDS system designed and implemented by Blanchfield for a large managed services provider, was one of the first sites in the world to detect and report the incident. Ed posted his original findings and info to various security lists and quickly wrote up a parser to create GDL files from Firewall and IDS logs, which he fed into aiSee Graph Layout Software in order to visually map this worm's effect on their customer's network. The first image is a visualization of log data for a class B firewall without background worm traffic, while the second represents the same data with background worm traffic. The graphs show just 15 minutes worth of traffic at midnight, but the impact of the worm is already clearly visible. You can imagine what 24 hours must have been like. |
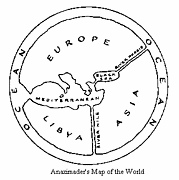 19 19 | print by Anaximander of Miletus (c. 610-546 BC), Turkey The first world map? No extant copies, but described in books II and IV of Herodotus "Histories." |
 22 22 | 1305 print by Ramon Llull (1235-1316), Spain Mechanical diagrams of knowledge, as aids to reasoning (served as an inspiration to Leibnitz in the development of symbolic logic). |
 23 23 | 1280 by Ramon Llull (1235-1316), Spain Triangular diagrams of paired comparisons for electoral systems (how to elect a Pope or Mother Superior, when all the candidates are voting). |
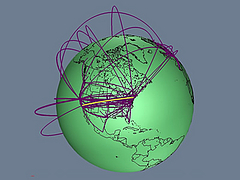
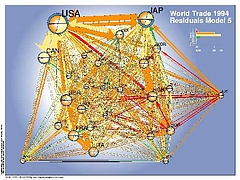
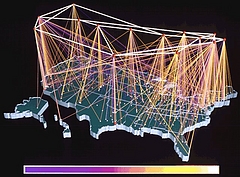 303 303 | 1992 computer graphics by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson, NCSA A fascinating Visualization Study of the NSFNET, undertaken by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson from the NCSA in 1992. |
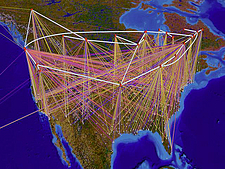 304 304 | 1992 computer graphics by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson A fascinating Visualization Study of the NSFNET, undertaken by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson from the NCSA in 1992. |
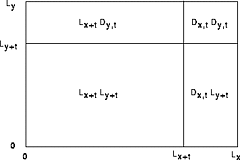
 629 629 | Voronoi Treemaps200510 computer graphics by Michael Balzer, Oliver Deussen Treemaps are a well-known method for the visualization of at- tributed hierarchical data. Previously proposed Treemap layout algorithms are limited to rectangular shapes, which causes prob- lems with the aspect ratio of the rectangles as well as with identify- ing the visualized hierarchical structure. The approach of Voronoi Treemaps presented in this paper eliminates these problems through enabling subdivisions of and in polygons. Additionally, this allows for creating Treemap visualizations within areas of arbitrary shape, such as triangles and circles, thereby enabling a more flexible adap- tation of Treemaps for a wider range of applications. ... Similarly to the other Treemap layout algorithms, enhancements like borders, adaptive edge sizes, cushions, coloring, etc., may also be applied to the described layout method. This additionally sup- ports the user in the perception and interpretation of the Treemap visualization. Examples for such enhanced Voronoi Treemap lay- outs are presented in Figures 10–12. Figure 10: Enhanced AW Voronoi Treemap layout of 4075 nodes at 10 hierarchy levels (a brighter color indicates a lower hierarchy level) Figure 11: Enhanced PW Voronoi Treemap layout of 16288 nodes at 7 hierarchy levels (a brighter color indicates a lower hierarchy level) |
 685 685 | computer graphics (PLankton) |
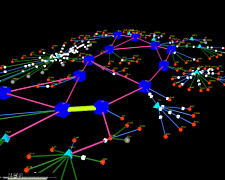
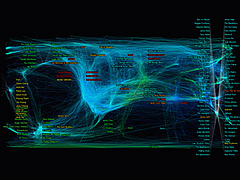
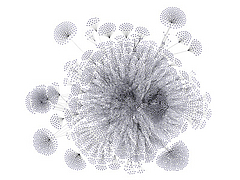 932 932 | 2005 computer graphics by (unknown) yFiles is an extensive Java class library that provides algorithms and components enabling the analysis, visualization, and the automatic layout of graphs, diagrams, and networks. The yFiles library offers the user many advantages, one of which is its ability to create, edit, and visualize large graphs with hundreds and thousands of elements. Here shown is a huge site map laid out and routed organically. For a large version of this image click here. |